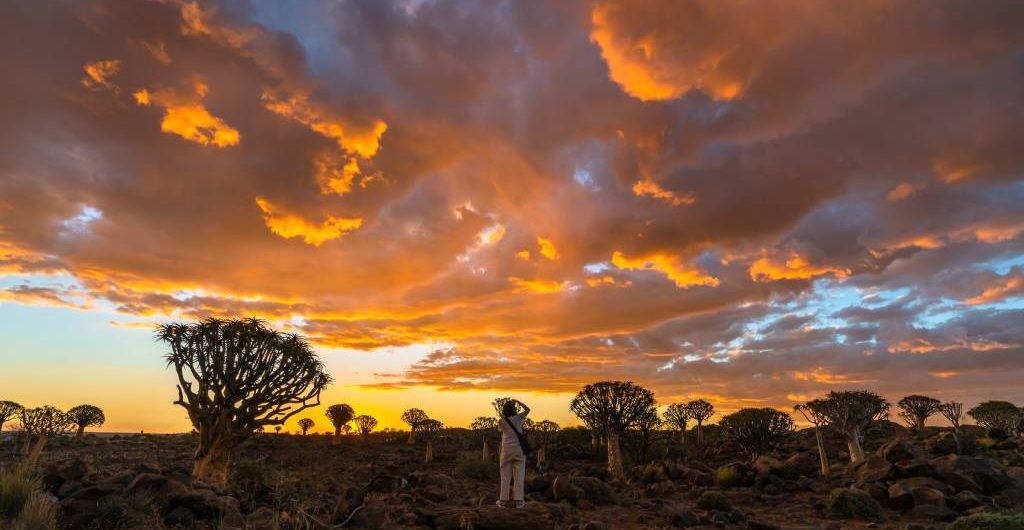

The world’s second-largest continent, is a vast and diverse landmass that holds a special place in global geography, culture, and history. Covering approximately 30.2 million square kilometers, it spans the equator and straddles both the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. Africa is not just a continent; it’s a tapestry of nations, peoples, landscapes, and stories.
Geographical Features

Africa’s geographical features are nothing short of awe-inspiring. The continent boasts a wide range of landscapes, from the vast Sahara Desert in the north to the lush rainforests of Central Africa and the savannahs of the Serengeti in the east. Towering peaks like Mount Kilimanjaro and the Atlas Mountains punctuate the landscape, while mighty rivers like the Nile, Niger, and Congo carve their paths through the continent. This diverse geography has given rise to an incredible array of ecosystems and wildlife, making Africa a biodiversity hotspot.
Historical Significance
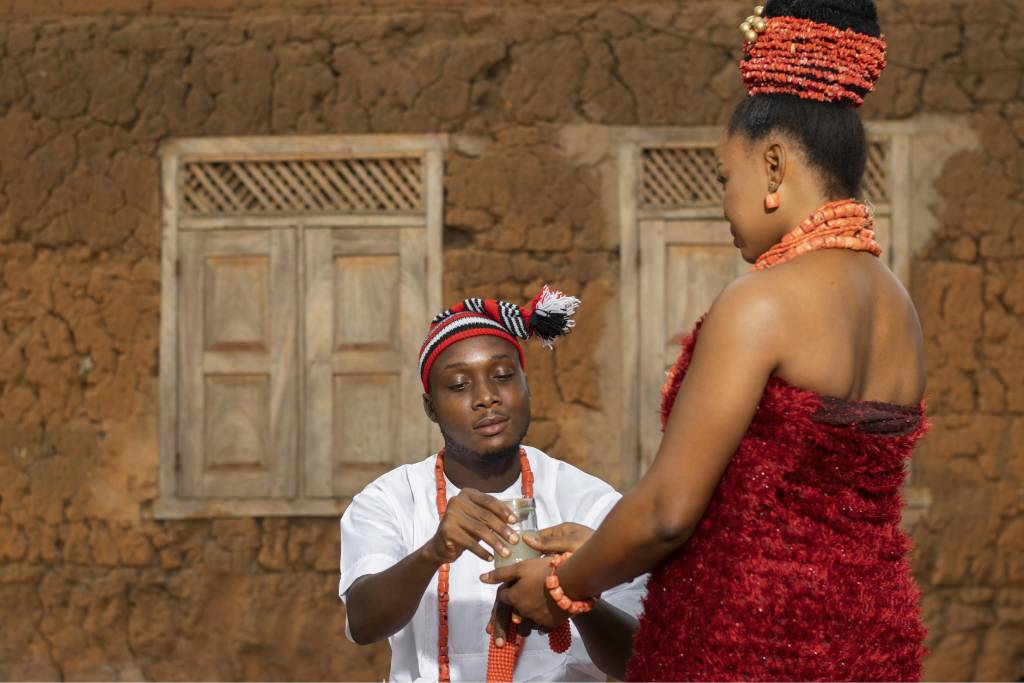

Africa has a rich and complex history that stretches back millennia. It is the birthplace of humanity, with evidence of early hominids found in places like the Great Rift Valley. Throughout antiquity, Africa was home to great civilizations such as Egypt, Nubia, Axum, and Mali, which made significant contributions to art, science, and culture.
Colonial Legacy and Independence
The colonial era left an indelible mark on Africa. European powers, driven by imperial ambitions, carved up the continent in the late 19th century. The consequences of this colonial legacy are still felt today, as borders were often drawn arbitrarily, disregarding the ethnic and cultural divisions that exist on the ground. However, the mid-20th century witnessed a wave of independence movements that led to the birth of many African nations, with leaders like Nelson Mandela, Kwame Nkrumah, and Jomo Kenyatta at the forefront of these struggles for self-determination.
Modern Africa
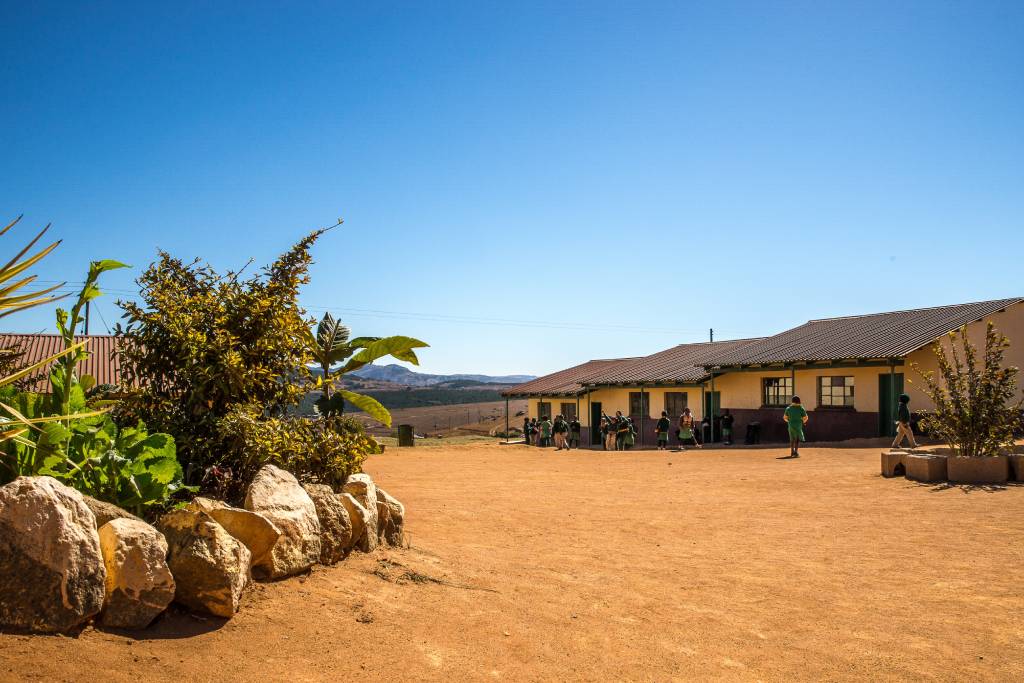

Today, Africa is a continent in motion. Its political map comprises 54 recognized countries, each with its own unique challenges and opportunities. While some nations have made significant progress in terms of political stability and economic growth, others continue to grapple with issues of governance, poverty, and conflict. The African Union, established in 2001, plays a pivotal role in promoting cooperation and development across the continent.
Society and Culture
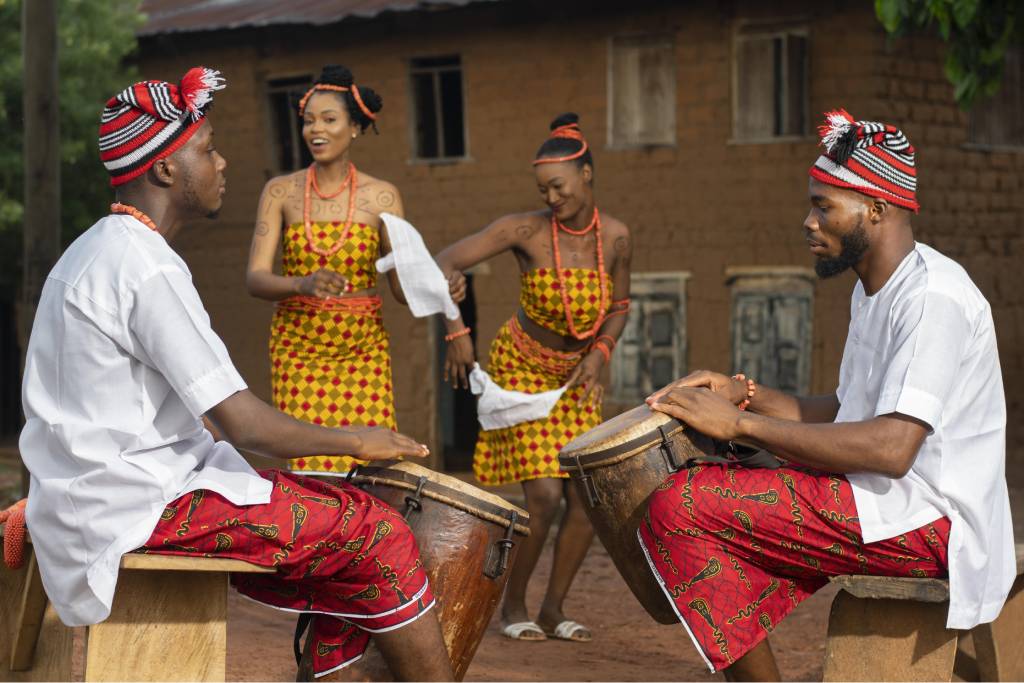

Africa’s cultural diversity is one of its most striking features. With over 2,000 distinct languages spoken and a myriad of ethnic groups, the continent is a mosaic of traditions, beliefs, and practices. Traditional African religions, Christianity, and Islam are all practiced, often alongside one another. The continent’s cultural richness is expressed through its art, music, dance, literature, and oral traditions, which have left an indelible mark on the global cultural tapestry.
Challenges and Opportunities
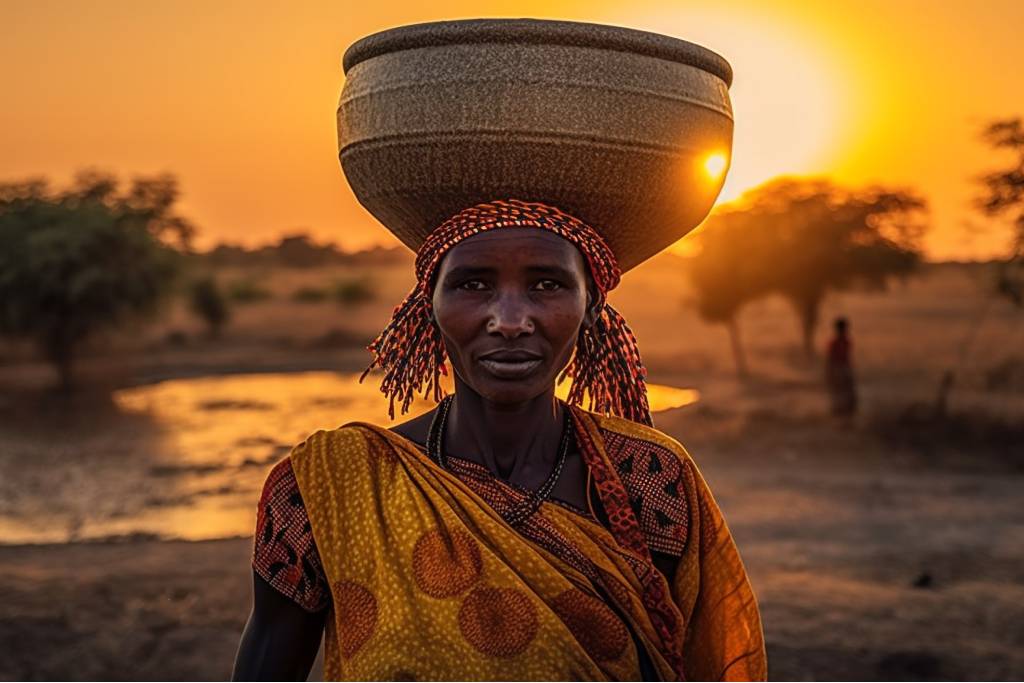

Africa faces a range of challenges, from poverty and inequality to health crises like HIV/AIDS and malaria. Political instability and conflicts persist in some regions, posing significant hurdles to development. However, Africa also holds immense potential. Its youthful population, vast natural resources, and a growing middle class make it a region of increasing economic importance on the global stage.